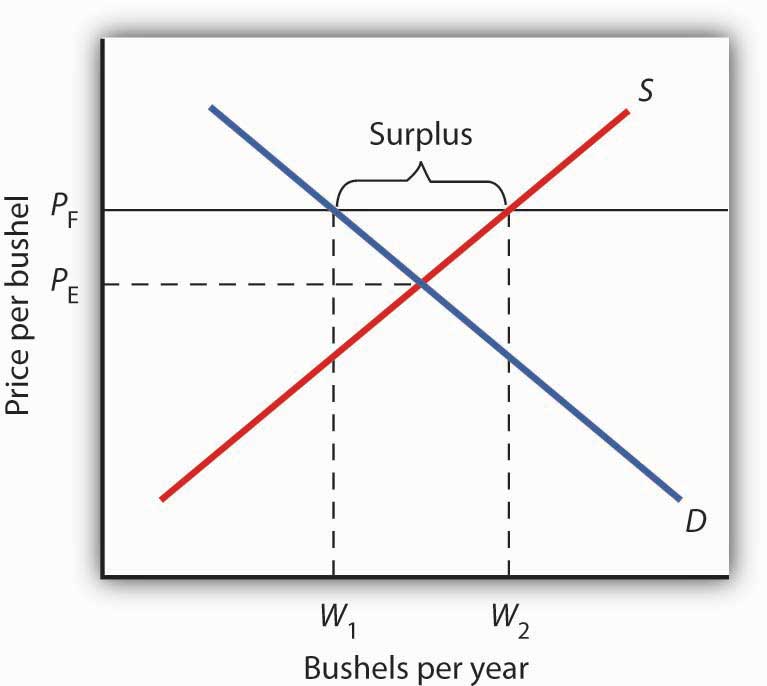
Consumers are always worse off as a result of a binding price floor because they must pay more for a lower quantity.
A price floor set above the equilibrium price is always be a binding price floor.
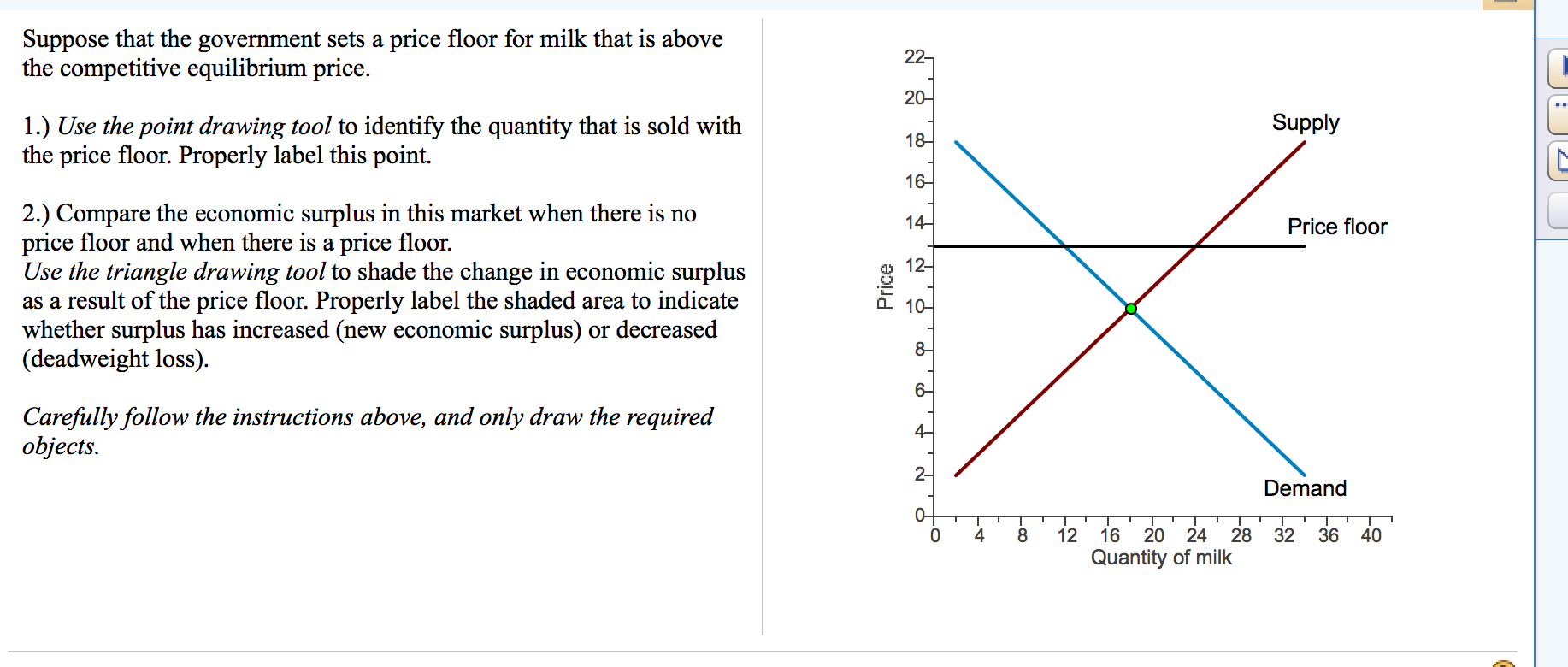
If a price floor that is above the equilibrium price is imposed on a market and the government buys the surplus what will happen to consumer and producer surplus.
Drawing a price floor is simple.
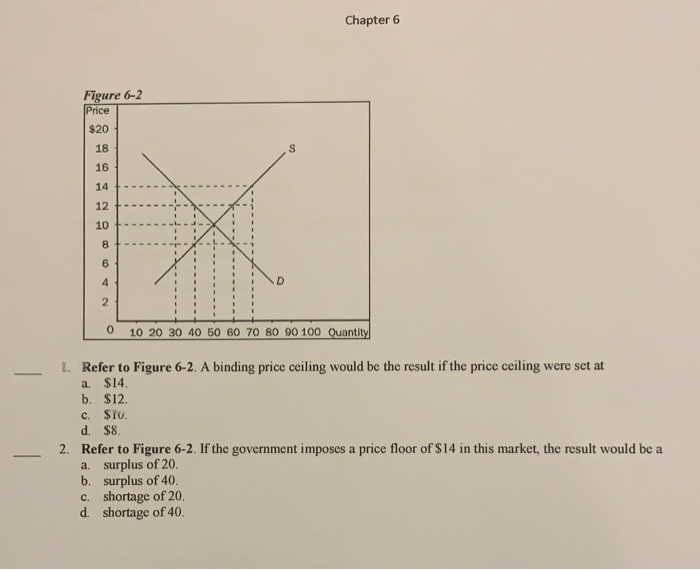
If the equilibrium price of gasoline is 3 00 dollars per gallon and the government places a price ceiling on the gasoline of 4 00 dollars per gallon the result will be a shortage of gasoline.
This graph shows a price floor at 3 00.
This has the effect of binding that good s market.
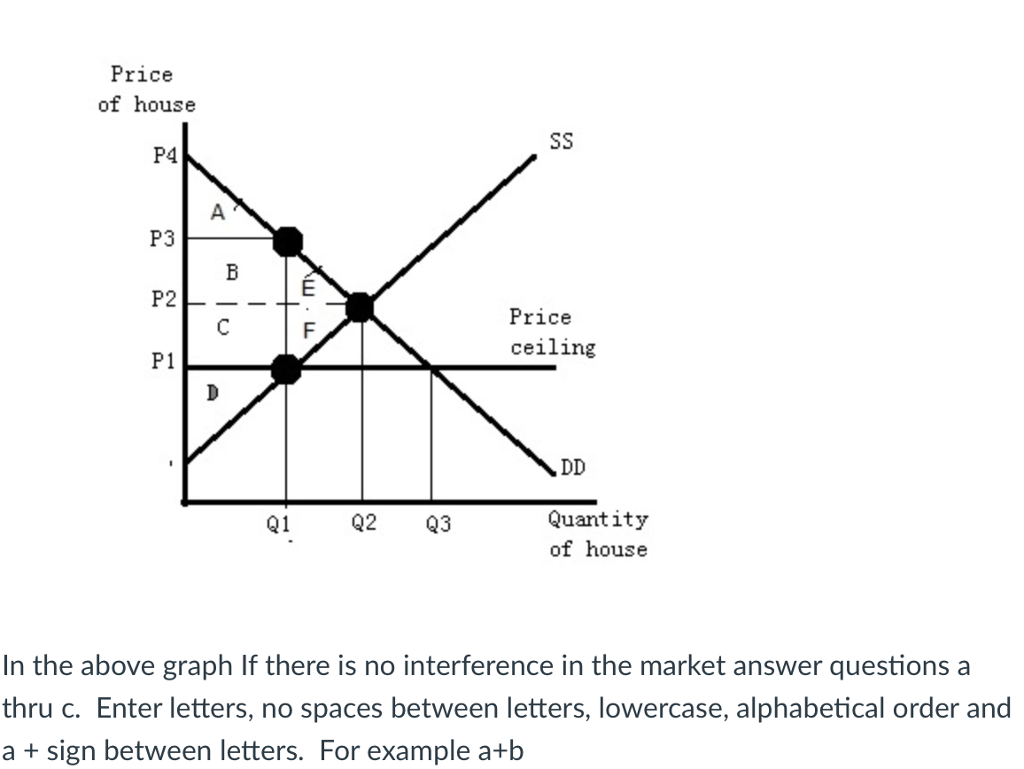
A price ceiling is a legal maximum price but a price floor is a legal minimum price and consequently it would leave room for the price to rise to its equilibrium level.
A minimum price set above the equilibrium price is a.
The government is inflating the price of the good for which they ve set a binding price floor which will cause at least some consumers to avoid paying that price.
Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level.
A binding price floor is a required price that is set above the equilibrium price.
This changes nothing because at this price there is a shortage which drives prices up.
Note that the price floor is below the equilibrium price so that anything price above the floor is feasible.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
Nothing is preventing prices from rising so nothing will change.
A non binding price floor is one that is lower than the equilibrium market price.
Another way to think about this is to start at a price of 100 and go down until you the price floor price or the equilibrium price.
In this case the market price would serve as a rationing mechanism because the price floor would have no effect on the market.
A price ceiling set above the equilibrium price is not binding.
The latter example would be a binding price floor while the former would not be binding.
For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price.
If there were a binding price floor in the market for milk the price could be.
In other words a price floor below equilibrium will not be binding and will have no effect.
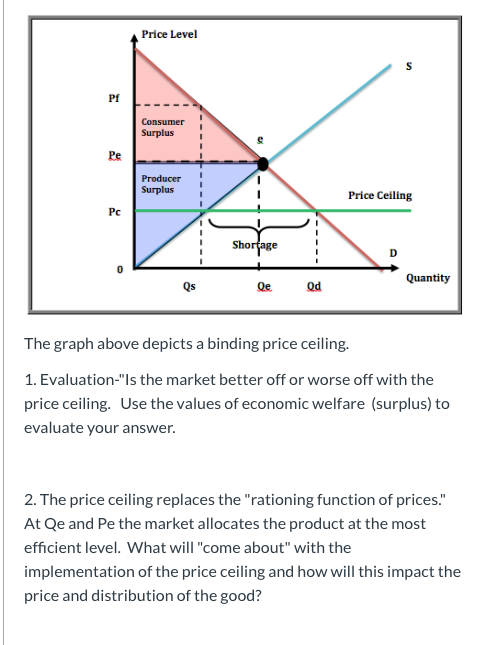
The equilibrium market price is p and the equilibrium market quantity is q.
If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant.
Look at the figure the market for milk.
A non binding price floor is set below the equilibrium price.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.